When trouble shooting a query in your report design, wouldn’t it be nice to be able to write the entire query out to your console or to a text control within your design, including the parameters? Or, maybe you want to write out the full queries that your users are running to a log file for monitoring.
If you are not using data set parameters, this is easy (and also unnecessary since the entire query text is static and available in the data set editor). You could just write the following script in a dynamic text control in your report design (or write it out to a log file or the console if running eclipsec.exe):
If you are using data set parameters, things are a little different.
With a query like:
You would get exactly that as your output, even after the user has entered parameter values or you’ve passed values through the data set parameters in another manner. The parameter values would not automatically replace the ‘?’ in the queryText property.
To get the values that are passed to the query, we can access the input parameter values from the data set’s afterOpen script with:
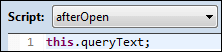
We can also access the queryText property from the afterOpen script with:
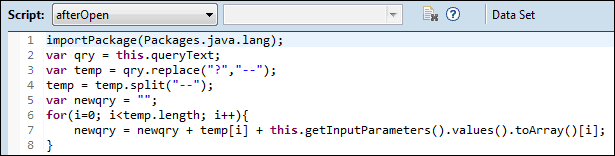
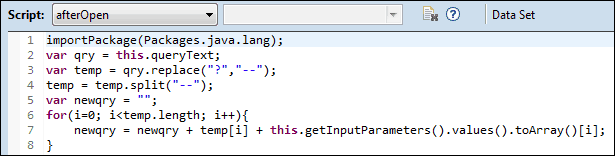
With a little script, we can take the queryText and replace the ‘?’ markers with the actual parameter values:
This script takes the query text, replaces the ‘?’ markers with ‘–‘ (this is done because the split does not work on the ‘?’), splits the query text where the parameter values need to be inserted, then loops through these query pieces combining them with the query values.
If you had more query after the last data set parameter, you would need to add the last piece of the query back, but for our example, this is not needed. This also does not handle the single quotes that would surround a string or a date. You’d have to handle that by checking the class of the value:
This will return “class java.lang.Integer”, “class java.lang.String”, etc. allowing you to handle the insertion of quotes.
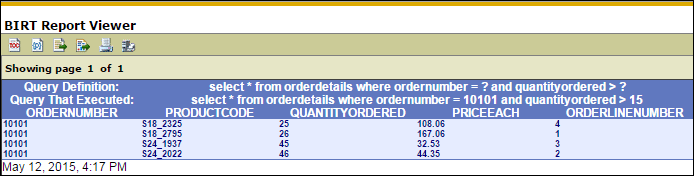
Now, we have our query with parameter values stored in the “newqry” variable to display in the report output, write to a log file, etc. In this example, we write it out to a global variable and recall it from a text control in the report, as you can see here:
Thanks for reading.